Mar 31.2022
Digital building and 7 technologies enable digitalization in construction sector
Digitalization of the construction industry is the implementation of digital technologies to transform existing business processes and services in construction production, companies, and construction supply chains.
Digitalization in the construction sector has great potential and can bring vast opportunities for the whole value chain. Besides improving existing practices, digitalization can benefit the industry by integrating disruptive technologies and tools that can lead to new processes, business models, materials, and solutions.

The technology landscape is changing rapidly. Following are some key technologies that enable digital transformation in recent days.
1. Building Information Modeling (BIM)
While there are different definitions of BIM, there is a common consensus that BIM describes the process of creating and managing digital information about a built asset. ISO 19650-1:2018 defines BIM as "use of a shared digital representation of a built asset to facilitate design, construction and operation processes to form a reliable basis for decisions". It brings new consistency and improves collaboration between construction professionals.
2. Digital Twins
Digital twins refer to the virtual representation of assets, processes, systems, and other entities. BIM and the digital twin strategy share many common principles, but it takes BIM to the next level with real-time data transmission. In traditional engineering construction, each stage of the project is relatively fragmented and less collaborative. In fact, the feasibility of construction and the implementation of the operational and maintenance stage results in many large numbers of reworks, delays and cost over-control. In the digital era, every house is "built twice" in the future, which means performing virtual construction of full-digitalization first and then performing physical construction. During the virtual construction, all participants work together to conduct digital proofing of the lifecycle process from intelligent design to virtual production, construction, and operational and maintenance. As a result, the team delivers a full-digital sample of optimal design scheme, feasible implementation scheme and reasonable business scheme. Then, through construction upgrading based on the digital twin to lean construction with planned construction processes, industrial-based physical buildings are built in the physical world to minimize project waste, maximize project value, and upgrade the construction to modern construction.
3. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI makes it possible for machines to emulate the way the human brain processes information and perform human functions. It is considered to be construction technology's next frontier. Although the relatively limited adoption so far, AI can facilitate a construction project through its life cycle, the potential of the technology is significant. Currently, the most common uses for AI in construction are scheduling and risk mitigation. For example, on-site behaviours can be monitored with the Internet of Things sensors, and the system can automatically warn of potential dangers before they cause serious problems.
4. Cloud Computing
Cloud computing allows the delivery over the 'cloud' (the internet) of a range of computing services, such as storage, databases, networking, servers, software and analytics. It means anyone with an internet-connected device can access stored data at any place, which facilitates collaboration among all stakeholders to improve the productivity of the project team.
5. Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT is the network of physical things embedded with technological software and devices that connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the Internet. IoT is closely related to sensors as in most cases it requires some form of data provided by the sensors. For instance, sensors can monitor smoke, temperature and alert management about potential dangers, and wearables can help labour management like on-site real-time positioning.
6. Robotics
Construction industry has a mixed feeling when it comes to robotics. Despite questions of taking over human jobs and pushing construction workers away from the sector, robotics undoubtedly have huge benefits on improving on-site safety, productivity, efficiency and flexibility. For instance, robots can free human workers from repeatative work and perform tasks in a dangerous environment or places inaccessible by human; drones can perform large-scale patrol work with few human operators or even automatically.
7. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
VR and AR are gaining popularity in recent years. AR can bring computer-generated objects into a physical environment, while VR refers to a simulated environment where an interactive computer-generated user experience can occur. They can be used in training to avoid risks to hurt workers or damaging the machinery. They also allow better collaboration with people on-site and work remotely and enable stakeholders to track progress with more accuracy.
Glodon Digital Building Strategy
Glodon defines the Digital Building as an industrial strategy that uses BIM, cloud computing, big data, IoT, mobile Internet, AI and other technologies to lead the industrial transformation and upgrading complemented by advanced lean construction. Through the effective integration of personnel, processes, data, technology and business systems, Digital Building allows the digitalization, networkisation and intelligentisation of the whole process with all the elements and participants of the industry, to structure a platform of a new ecological system that involves projects, enterprises, and industries. This cooperation will drive the industrial upgrade towards new design, construction and operational & maintenance method and contribute to the industrial goals of making every project a success.
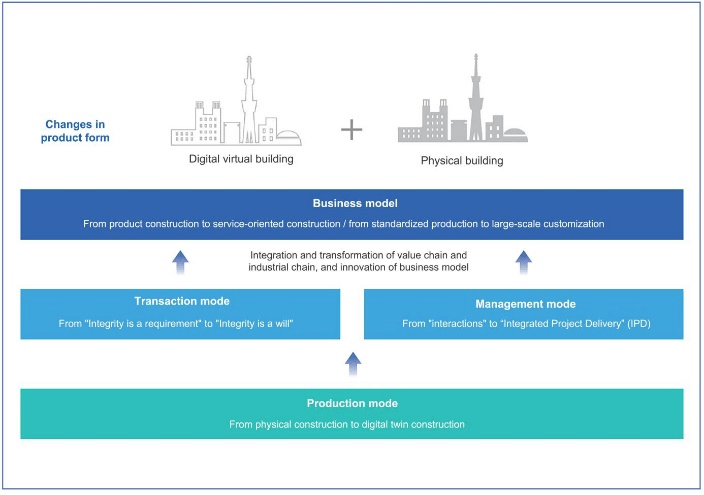
Moreover, implementing Digital Building benefits construction enterprises that consequently improve quality and efficiency, reduce costs and energy consumption, and create value innovation. This integrated catalytic effect of the digital technologies with the traditional building industry forms a new system that incorporates processes, elements, and participants whilst digitalization, online operation, and intelligence build up a new industry.
In addition, a new Digital Building industry is created that establishes new productivity with integrated new design, new construction and new operation and maintenance (based upon digital transformation). This focuses on customers' needs and a better connection between the demand and supply through digitalization. Henceforth, among others fully digitised samples are produced; industrialised construction and intelligent operation and management services are offered; continually promoting innovation on the product, business and organisation are achieved, as well as pre-identification of uncertainties and risks.